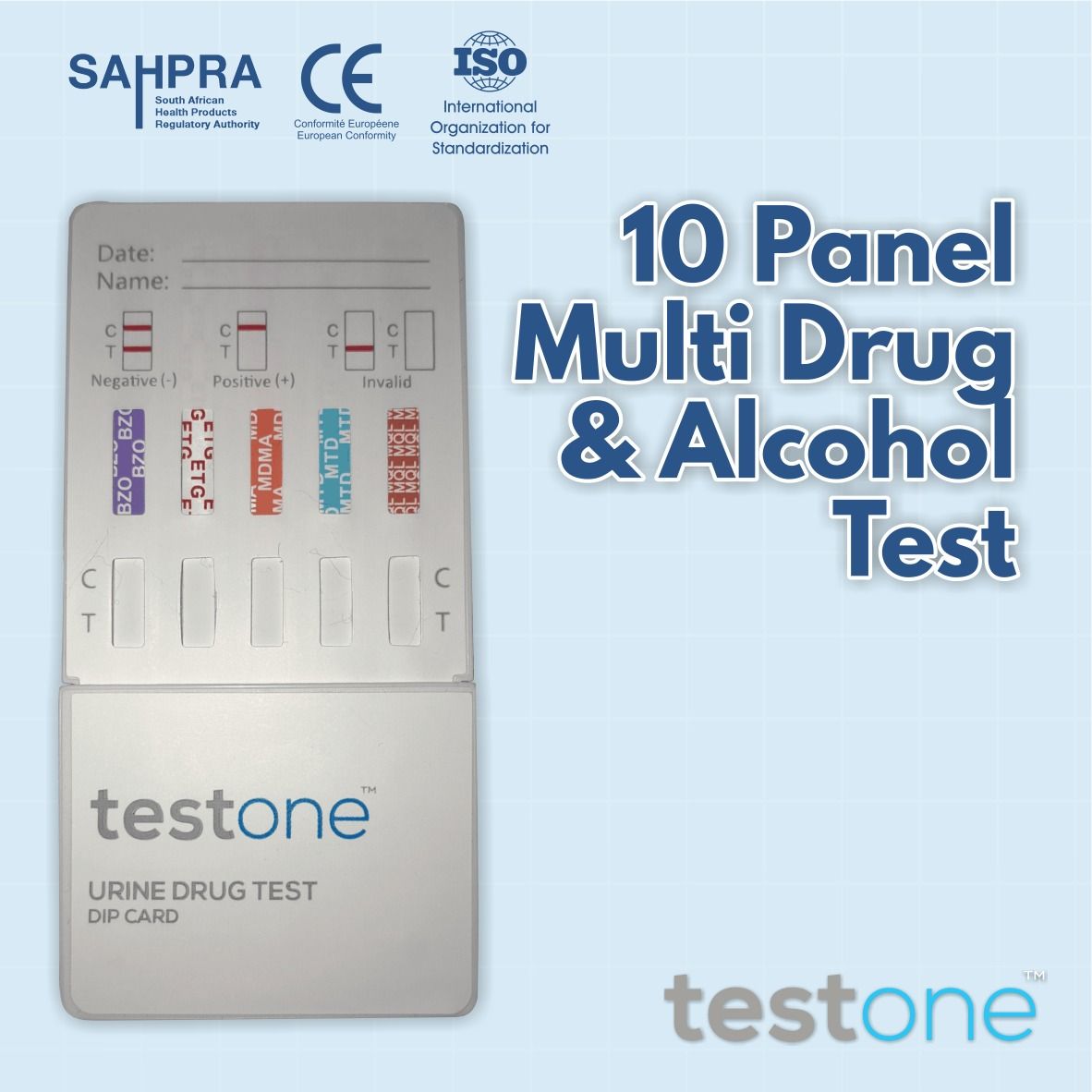
10 Panel Multi Drug and Alcohol Test Dip Card Minimum 100 Device: Dip Card Specimen : Urine Drugs Tested: 9 Drugs + Alcohol Brand: Test One 10 Multi Urine Drug Test Dip Card is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of 9 drugs and drug metabolites+ Alcohol in urine at a cut-off concentration ABBREVIATION DRUG Cut-Off EXAMPLES DRUGSDETECTED CERTIFICATE (AMP) Amphetamines 1000ng/ml ADHDSpeedKhat CE0123 (COC) Cocaine 300ng/ml Crack Cocaine , Powder CE0123 (MET ) Methamphetamines 1000ng/ml Crystal MethTikDesoxyn CE0123 (OPI) Opiates 2000ng/ml Heroin Codeine TylenolVicodin CE0123 (THC) Marijuana 50ng/ml Dagga Marijuana CE0123 (BZO) Benzodiazepines 300ng/ml Sleeping TabletsOxazepam XanaxAtivan Rohypnol CE0123 (ETG) Ethyl glucuronide 500ng/ml Alcohol Mouth WashVanilla ForensicUse MDMA Methylenedioxymethamphetamine 1000ng/ml Ecstacy CEO123 MTD Methadone 300ng/ml Methadone CEO123 MQL Methaqualone 300ng/ml Mandrax , Buttons CEO123 Features & Benefits: The only Multi Drug Test , testing for drugs and alcohol simultaneously Our 7 PanelMulti Drug Tests with a new ETG AlcoholPanel are perfect for schools , work place , medical aids , healthcare practitioners& drug and alcohol rehabilitation centers who have a zero tolerance alcohol policy Longdetection window of up to 80 hours post alcohol consumption, depending on amount of alcohol intake. Our Tests are CE , FDA and TUV approved. Manufacturer Complies with ISO Factory standards ISO9001ISO13456 100% Return/ Refund Policy within 7 days of purchase. Great All in One Test . Don’t have to buy separate tests 99% Accurate Highly accurate results when compared to GCMS lab test Gives individual results for each drug type listed above Amphetamines Amphetamines are central nervous system stimulating drugs. Overdose or extended usage may lead to substance abuse. Amphetamine abuse may cause severe or permanent damage to the human nerve system. Amphetamines appear in the urine within three hours of administration. It may be present for about 24-48 hours. Cocaine Cocaine is a nervous system stimulating drug. It has pharmacological properties such as local anesthetic. It has addictive effects. It may lead to substance abuse. Cocaine may appear in urine for only few hours after use. Benzoylecgonine is a metabolite of cocaine. Benzoylecgonine may be detectable in urine over 2 days after taking cocaine. Its detection in human urine has been widely used to evaluate cocaine usage. Methamphetamines Methamphetamine overdosage causes restlessness, confusion, anxiety, and coma. Chronic abusers may develop paranoid psychosis. D-Methamphetamine is used in the treatment of obesity. Its duration is 2-4 hours. In normal conditions up to 43% of methamphetamine is eliminated unchanged in the 24-hour urine and about 4-7% as amphetamine. In acid urine, up to 76% is parent drug and 7% is amphetamine in 24 hours. In alkaline urine there is 2% parent drug and less than 0.1% amphetamine in 24 hours. Opiates Opiate refers to any drug that is derived from the opium poppy, including the natural products, morphine and codeine, and the semi-synthetic drugs such as heroin. Opioid is more general, referring to any drug that acts on the opioid receptor. Opioid analgesics comprise a large group of substances which control pain by depressing the central nervous system. Large doses of morphine can produce higher tolerance levels, physiological dependency in users, and may lead to substance abuse. Morphine is excreted unmetabolized, and is also the major metabolic product of codeine and heroin. Morphine is detectable in the urine for several days after an opiate dose. Marijuana Tetrahydrocannabinol is known as THC, Δ-9-THC, Δ-1-THC. It is the most active of the principal constituents and major metabolite of cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are a group of compounds including marijuana and hashish. Cannabinoids have been used as central nervous system depressants. Overdose and extended usage may lead to substance abuse. Cannabinoids abuse may cause severe or permanent damage to the human nerve system. The detection of THC in human urine has been widely used to assess cannabinoids abuse. Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines are anxiolytic drugs that are most widely prescribed and used as anti-anxiety agents. They are also used as hypnotics, muscle relaxants and anticonvulsants. Some metabolites of benzodiazepines also exhibit pharmacological activities. Use of benzodiazepines can result in drowsiness and confusion; it also potentiates alcohol and other central nervous system depressants. Psychological and physical dependence on benzodiazepines can develop if higher doses of the drug are given over a prolonged period. Benzodiazepines are taken orally or by injection. The drug is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine as the parent compound or as oxazepam (in the case of chlorodiazepoxide and diazepam). Oxazepam is detectable in the urine for up to 7 days. ETG Ethyl Glucuronide (ETG) is a metabolite of ethyl alcohol which is formed in the body by glucuronidation following exposure to ethanol, such as by drinking alcoholic beverages. It is used as a biomarker to test for ethanol use and to monitor alcohol abstinence in situations where drinking is prohibited, such as in the military, in MDMA Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) is a designer drug first synthesized in 1914 by a German drug company for the treatment of obesity.5Those who take the drug frequently report adverse effects, such as increased muscle tension and sweating. MDMA is not clearly a stimulant, although it has, in common with amphetamine drugs,a capacity to increase blood pressure and heart rate.MDMA does produce some perceptual changes in the form of increased sensitivity to light, difficulty in focusing, and blurred vision in some users. Its mechanism of action is thought to be via release of the neurotransmitter serotonin. MDMA may also release dopamine, although the general opinion is that this is a secondary effect of the drug (Nichols and Oberlender, 1990).The most pervasive effect of MDMA, occurring in virtually all people who took a reasonable dose of the drug, was to produce a clenching of the jaws. The Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Urine) yields a positive result when the concentration of Methylenedioxymethamphetamine in urine exceeds 500 ng/mL. At present, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) does not have a MTD Methadone is a narcotic analgesic prescribed for the management of moderate to severe pain and for the treatment of opiate dependence (heroin, Vicodin, Percocet, morphine). The pharmacology of oral methadone is very different from IV methadone. Oral methadone is partially stored in the liver for later use. IV methadone acts more like heroin. In most states you must go to a pain clinic or a methadone maintenance clinic to be prescribed methadone. Methadone is a long acting pain reliever producing effects that last from twelve to forty-eight hours. Ideally, methadone frees the client from the pressures of obtaining illegal heroin, from the dangers of injection, and from the emotional roller coaster that most opiates produce. Methadone, if taken for long periods and at large doses, can lead to a very long withdrawal period. The withdrawals from methadone are more prolonged and troublesome than those provoked by heroin cessation, yet the substitution and phased removal of methadone is an acceptable method of detoxification for patients and therapists. MQL Methaqualone (Quaalude, Sopor) is a quinazoline derivative that was first synthesized in 1951 and found clinically effective as a sedative and hypnotic in 1956.10It soon gained popularity as a drug of abuse and in 1984 was removed from the US market due to extensive misuse. It is occasionally encountered in illicit form, and is also available in European countries in combination with diphenhydramine (Mandrax). Methaqualone is extensively metabolized in vivo principally by hydroxylation at every possible position on the molecule. At least 12 metabolites have been identified in the urine. The Multi-Drug Rapid Test (Urine) yields a positive result when the